
Study: Sport Specialization Increases Risk of Injury in Young Athletes
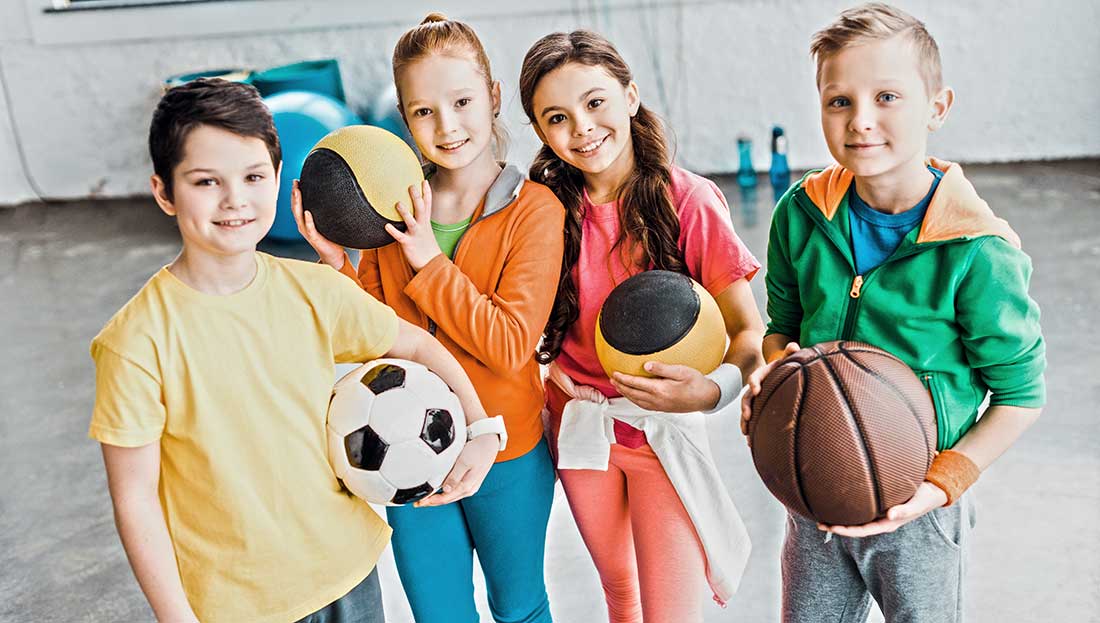

A new study finds that kids who specialize in a chosen sport tend to engage in higher levels of vigorous exercise than their peers, which sounds like good news given that so many children don’t achieve the recommended amount of physical activity. Unfortunately, these same kids also may be more likely to sustain injuries, such as stress fractures, tendinitis and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears.
The findings, which draw from a multiyear, ongoing study of 10,138 older children and teens living throughout the United States, suggest that volume of vigorous activity is a strong predictor of injuries for both boys and girls. In other words, those who engage in the most hours of intense activity per week are the most likely to be injured.
“It’s wonderful for a child to love a sport and to want to engage in it, but we must keep in mind the number of hours spent playing,” says study author Alison Field, a professor of epidemiology and pediatrics at Brown University. “They add up pretty quickly.”
She hopes the study’s conclusions will help coaches, parents and doctors guide young athletes toward less intense, less specialized training.
This study, published in the Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine, helps to explain some of the dangers of sports specialization. Athletes who focus on one particular sport tend to practice more frequently and intensely compared to athletes who do not.
“But if we send out a message that says kids shouldn’t specialize, the worry is that parents and kids will just add another sport on top,” Field says. “So they’ll keep their current sport and do it at a very high level and just add one more sport so they’re not ‘specializing.’ That would really increase their volume, so it probably would not be a good idea.”
Instead, Field says the best recommendation is to moderate the amount of time young athletes spend engaging in vigorous physical activity—and if they must specialize in a sport, replace some of their training with different forms of exercise, such as yoga and conditioning.
Field says a common fear among parents is that if their children don’t play more and more, they’ll fall behind in their sport and won’t ultimately be as good of an athlete.
“But it may actually be the opposite,” she said. “If children do too much, they may get injured and fall behind. And it’s important also to remember that they should enjoy doing their sport; it should be something that doesn’t overwhelm their life.”
Does Gender Increase Risk?
The study also suggests that sports specialization carries risks even when considered separately from volume of activity. These risk patterns differed for girls versus boys. For girls, once volume was accounted for, no particular sport stood out as being extra risky to specialize in. However, specialization in general increased girls’ risk of injury by about 30%.
In contrast, specialization in general did not significantly increase boys’ risk of injury, once volume was accounted for. But certain sports—baseball and gymnastics/cheerleading—did increase their risk.
Field says the precise reasoning behind the gender differences in risk is not yet clear, but it’s an area the researchers hope to explore further in future studies. For girls in particular, they also plan to examine age-related differences.
“There’s been a lot of concern about females having higher risk of certain injuries,” Field explains. “The question is: Is that risk highest just as they’re going through their pubertal growth spurt, and then does it come back down a bit? And then we need to talk to coaches and trainers and say, ‘What can we do to mitigate that risk?’”
What Does the Research Mean to Health and Exercise Professionals?
As a health and exercise professional, you are a source of knowledge and experience for your clients. If you train youth athletes, their parents undoubtedly turn to you for advice on everything from when their child should start strength training to what foods should be eaten or avoided before a game or competition. If you notice the signs and symptoms of overtraining or burnout in a child, it is essential that you alert his or her parents right away. While these signs include increased incidence of injuries and illness, you should be aware of other, less obvious signs. These include increased resting heart rate, impaired physical performance, reduced enthusiasm and desire for training, altered appetite, disturbed sleep patterns and irritability.
“While parents might be trying to help their kids get a head start on development in a particular sport, it is important that parents gain an understanding of the importance of youth athletes developing overall athleticism,” urges Michael Piercy, MS, CSCS, founder of The LAB, based in Fairfield, N.J. “With a focus on overall athleticism in a program of long-term development, young athletes will gain fundamental skills and develop good general athletic skills that are needed later on when specialization becomes an appropriate training focus.”
Piercy urges health and exercise professionals to take the time to explain and educate parents on the risks of overspecialization. In doing so, he says, you can “help young athletes join programs that will instill a variety of athletic skills that can lead to success in multiple sporting disciplines, while avoiding youth athlete burnout, poor social relationships and premature peaking of athletic skill development.”
Expand Your Knowledge

Long-term Athletic Development in Youth [recorded webinar]
Learn fun, innovative ways to build skill development, functional speed and agility into sessions for your youth athletes so you can enhance their overall athleticism.

ACE Youth Fitness Specialist [specialist program]
As an ACE Youth Fitness Specialist, you’ll help the youngest generation get moving and get healthy.
Youth Resistance Training: Programming Tips for Exercise Professionals [blog article]

More Articles
- Certified™: November 2019
ACE-SPONSORED RESEARCH: Muscle Activation During Battle Rope Exercises
Contributor
- Certified™: November 2019
Hustle, Hustle, Hustle: How to Avoid Feeling Overwhelmed as a Fitness Entrepreneur
Health and Fitness Expert
- Certified™: November 2019
Understanding the Barbell Hip Thrust
Health and Fitness Expert
- Certified™: November 2019
The Case for Behavior-change Coaching in Diabetes Prevention
Health and Fitness Expert



 by
by 

